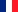
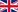
Lobular breast carcinomas are more challenging to detect through imaging than infiltrating ductal carcinomas, whether in mammography, ultrasound, MRI, or PET with 18F-FDG. Indeed, the 18F-FDG PET/CT often shows low contrast for the primary tumor. However, lobular cancers express more of the FAPα (Fibroblast Activation Protein α) than ductal carcinomas, making the use of 68Ga-FAPI PET promising for this indication.
The GALILEE project, led by Dr. Florent Hugonnet (Nuclear Medicine Department, Princess Grace Hospital Center, Monaco), aims to compare 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT with 18F-FDG PET/CT in the initial staging of lobular breast cancers. Through advanced analysis of PET images obtained with both radiotracers, we seek to establish a link between the extracted radiomic features and the histological characteristics of the lesions.
The ARAMIS project (Emergence, Cancéropôle Ile-de-France) aims to develop an artificial intelligence algorithm capable of automatically analyzing FDG PET scans in oncology. The goal is to better understand and predict the cancer progression by extracting relevant information from the images, such as the features from tumor lesions and non-tumor tissues. Using an unsupervised learning algorithm, ARAMIS will explore a latent space that can structure and interpret the data from PET scans.
The project relies on a retrospective database of over 4,000 PET scans from patients with various types of cancer. The analysis of this latent space will allow the development of a classifier capable of automatically identifying the organ of origin of the cancer and addressing other complex tasks, such as predicting treatment response or patient survival.
Photo Dynamic Therapy (PDT) is a localized treatment using a laser beam focused on the tumor. The PDT is based on the activation by specific wavelength light of a photosensitizer (PS) localized preferentially in tumor cells.